Research: AI Powered Historical Book Question Answering

Research: AI Powered Historical Book Question Answering
Abstract
In the recent past, we have seen a number of approaches, datasets, models, and even large language models (LLM) used for question-answering. The results of these initiatives are very encouraging, but generating questions from the given document, and generating a correct answer to a given question from a given document, is still challenging. It becomes more challenging when the text is historical, and it is translated from another language and a different script is used to write the translation than the script of the original text. This problem is because of the spelling of nouns in the original script. Secondly generating description answers and evaluating the correctness of descriptive answers is a challenge. Thirdly, if n number of question-answer pairs are generated from a certain corpus then how do you measure the performance of this model? Finally, if we have a large body of text and some questions in our mind then without giving the context how to get the answer? In this work, we are exploring techniques for creating questions and answers for a book corpus using ChatGPT and other available techniques, we call this QAGS. Secondly, we are finetuning the t5, flan-t5 model for creating an answer generation system, we call this AGS. Thirdly we are retrieving a relevant document that can answer a question in our hand, we call this DRS. Finally, we are creating and evaluating a system that can answer a history question without any context, we call this RAAGS. In this work, we are using The Mahabharata book as a corpus. To evaluate the different sub-systems we have used different metrics like BLEU, ROUGE, Accuracy, Recall, R@n, P@n, F1@n, Cosine. We have used SentenceTransformer for text embedding. Our approach does not depend upon the domain, script, or language of the text document. Neither, does it depend upon the Era when the text was written. It doesn’t need any manual feature engineering of the text. We have explored SOTA transformers like T5, distilBERT, RoBERTa, Bloom, BERT, BigBird from huggingface for zeroshot learning. The cosine between answer \& question, answer \& chunk is 0.91. In DRS MRR metric is 0.55, and MAP is 0.25. In AGS cosine between the reference answer and predicted answer is 0.827. In RAAGS cosine between the reference answer and the predicted answer is 0.763
Technology Used
- LLM/LLM-API: ChatGPT, ChatPDF, LlaMa2 (PEFT & LoRA), BLOOM, PaLM
- Transfromers & Frameworks: BERT, T5, FlanT5, GPT2, ChatGPT, ChatPDF, DistilBERT, RoBERTa, PyTorch, Huggingface, Kaggle, Colab, LangChain, RAG
- Machine Learning Libraries: NLTK, RE, Pandas, Scikit-Learn, Seaborn, Wordcloud, Markdown, Python, Selinium, numpy,
- Embedding & Pretrained Emb. Models: sentence-transformers, multi-qa-distilbert-cos-v1, all-MiniLM-L6-v2, all-distilroberta-v1, multi-qa-mpnet-base-dot-v1, all-roberta-large-v1
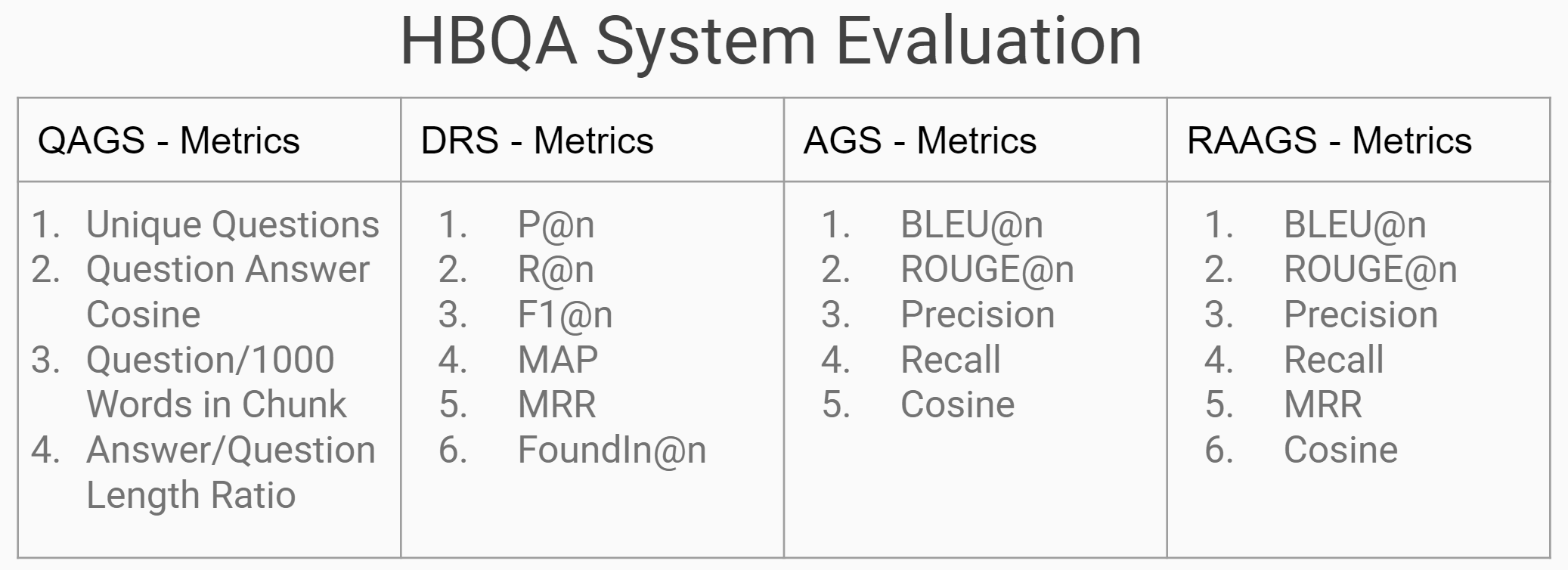
- NLP Eval: google_bleu, GLEU, ROUGE, Cosine, R@n, P@n, F1@n, MRR
Approach
HBQA Overall Approach
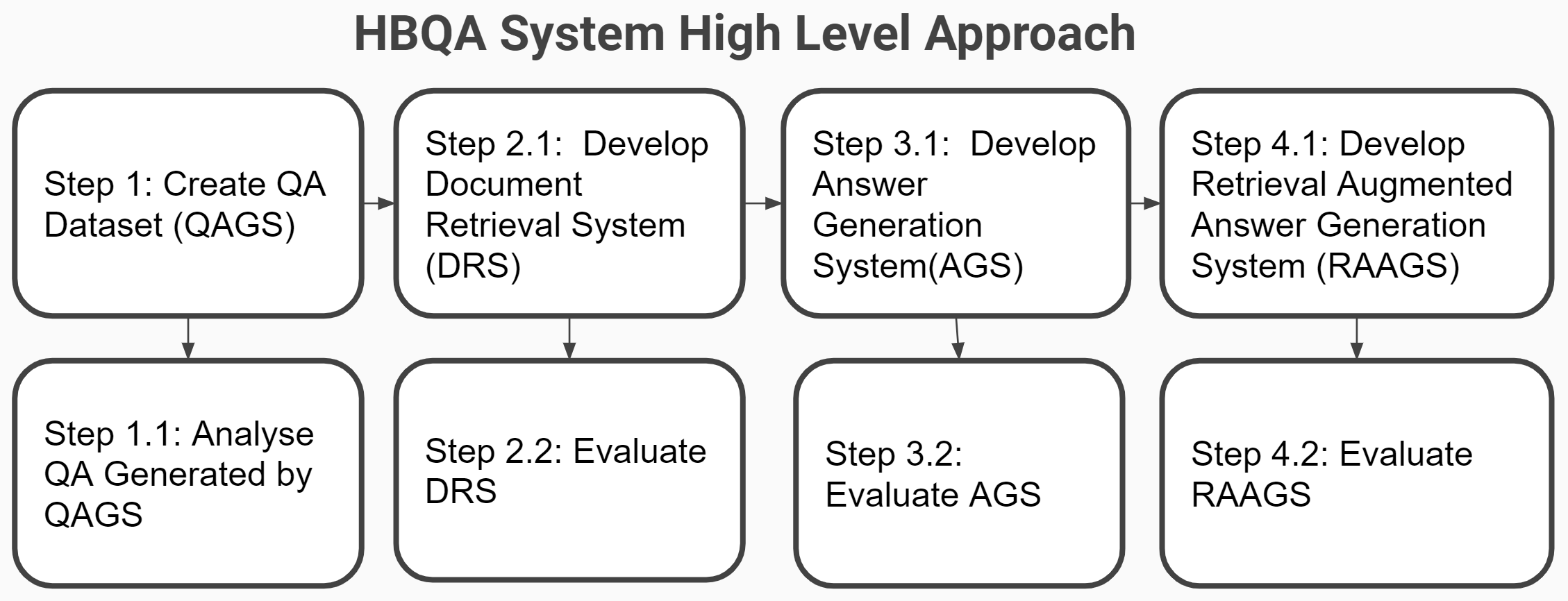
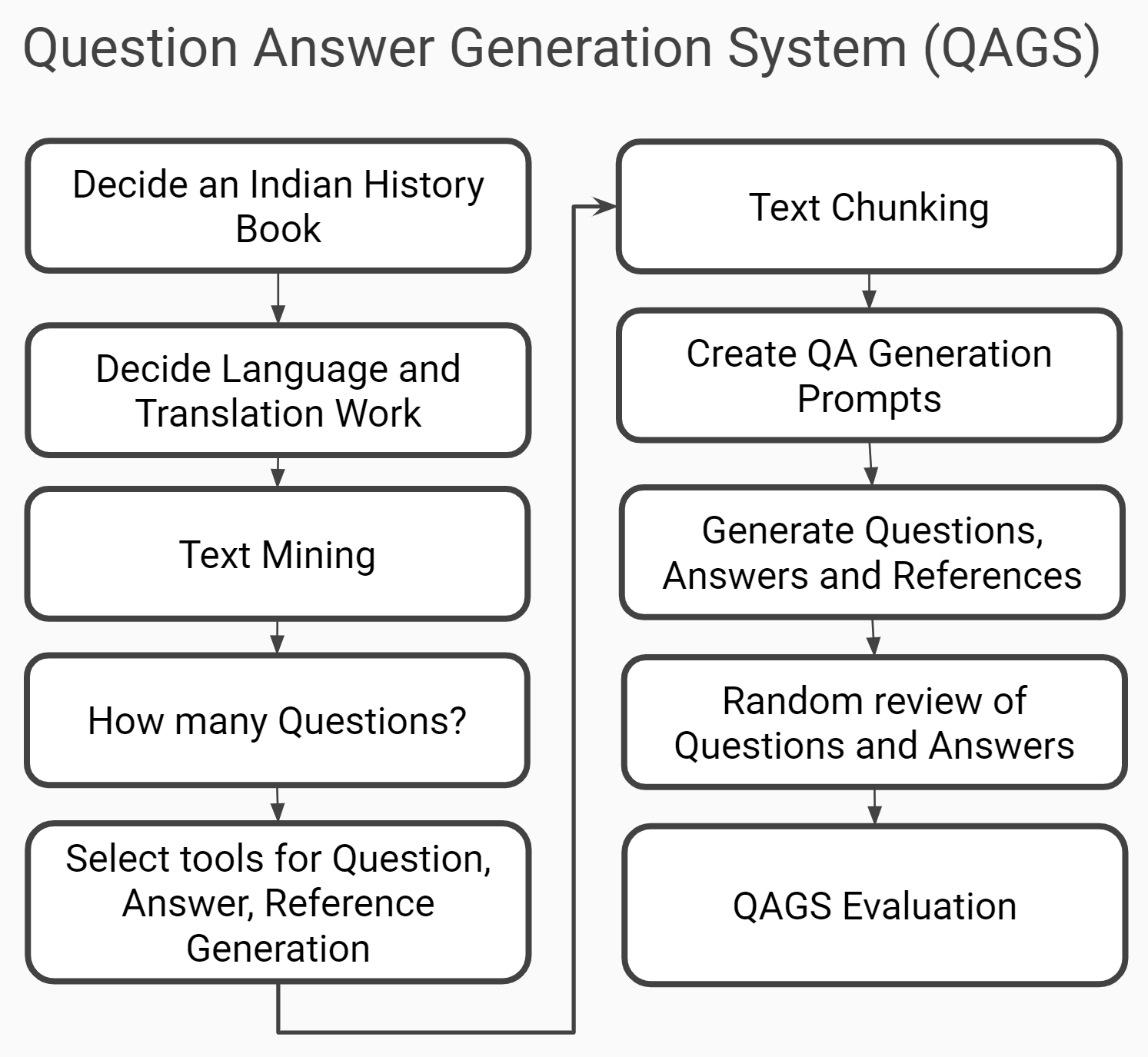
Question Answer Generation Systerm
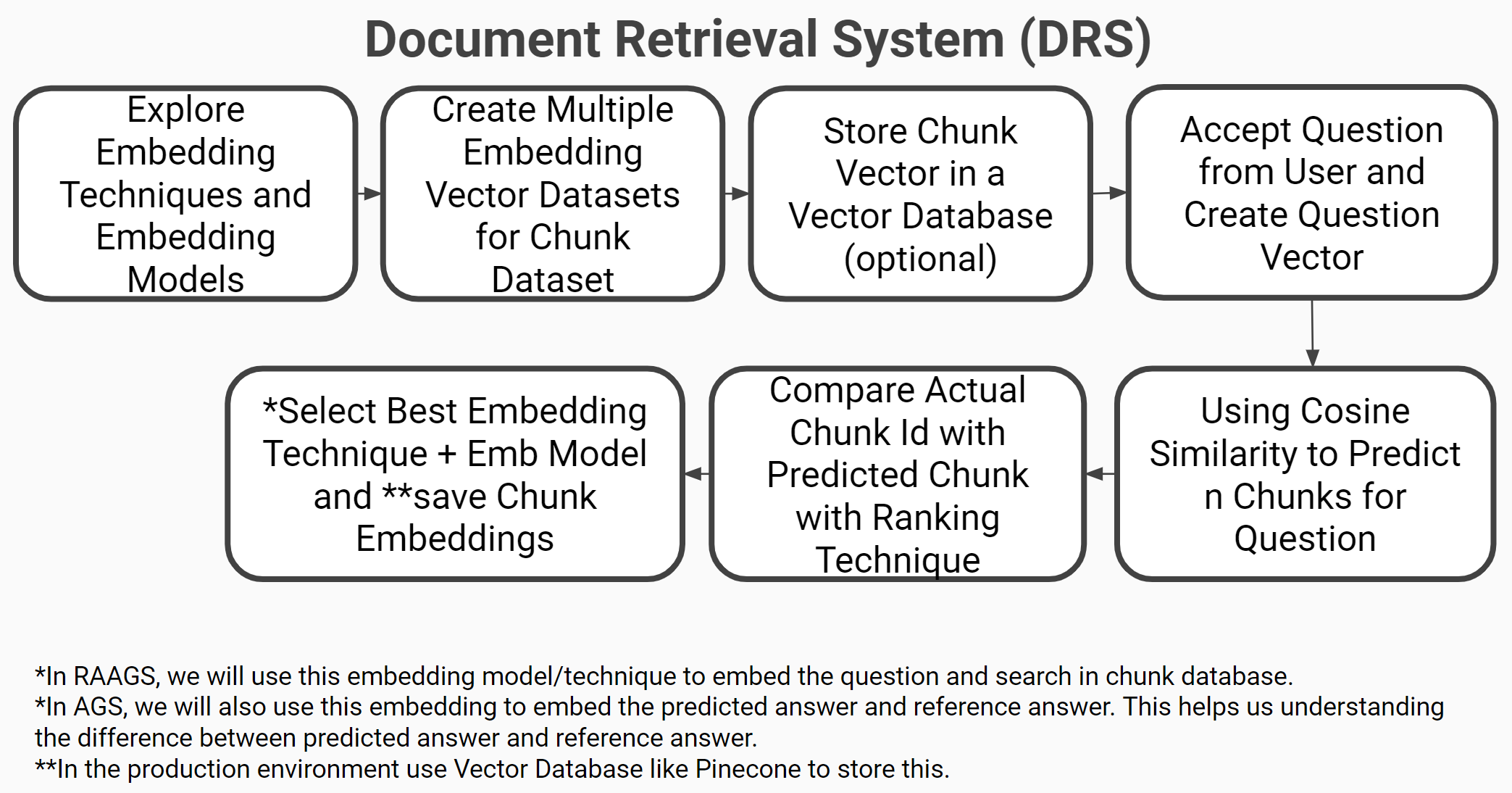
Document Retrieval Systems
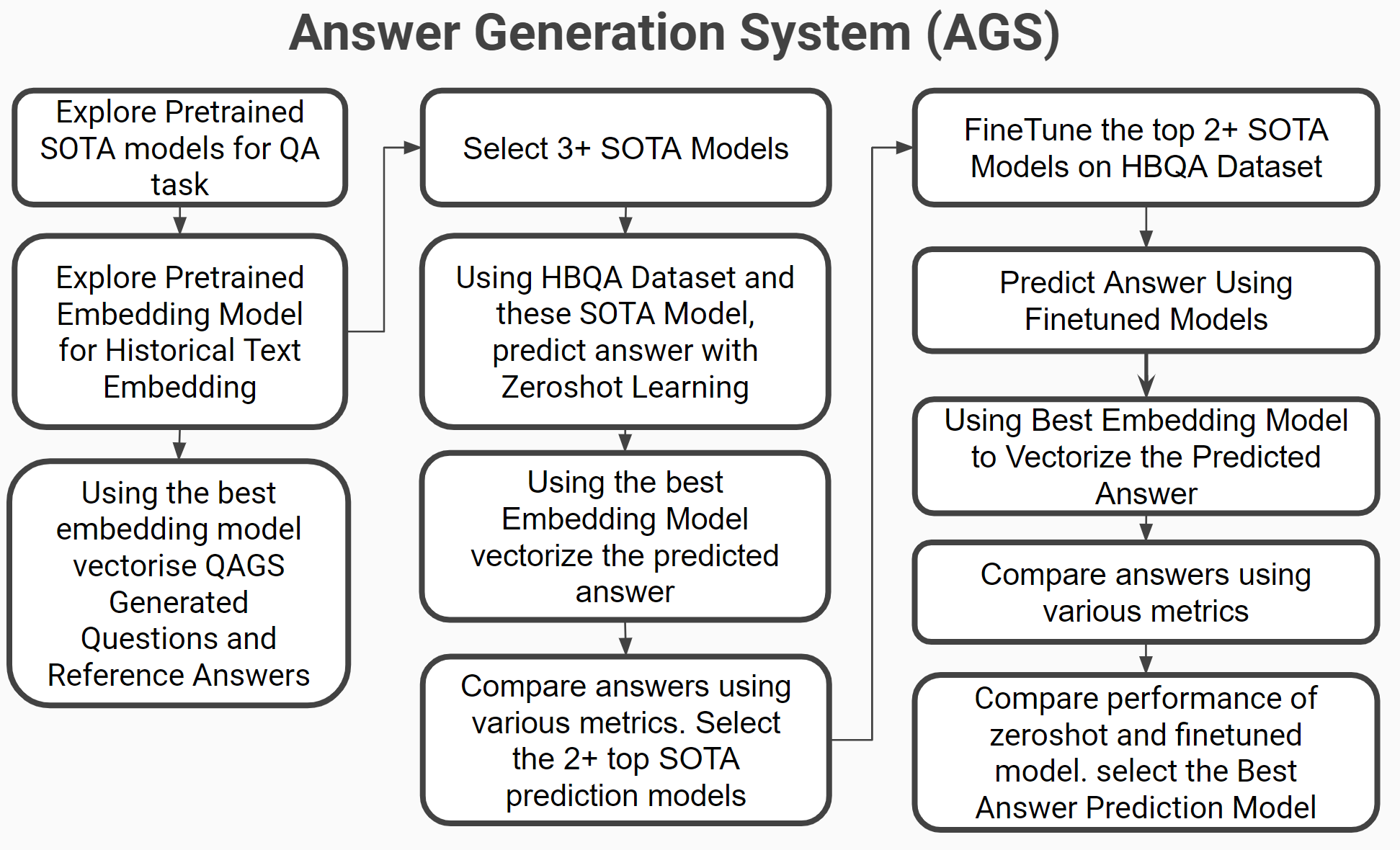
Answer Generation System
Retrieval Augmented Generation System
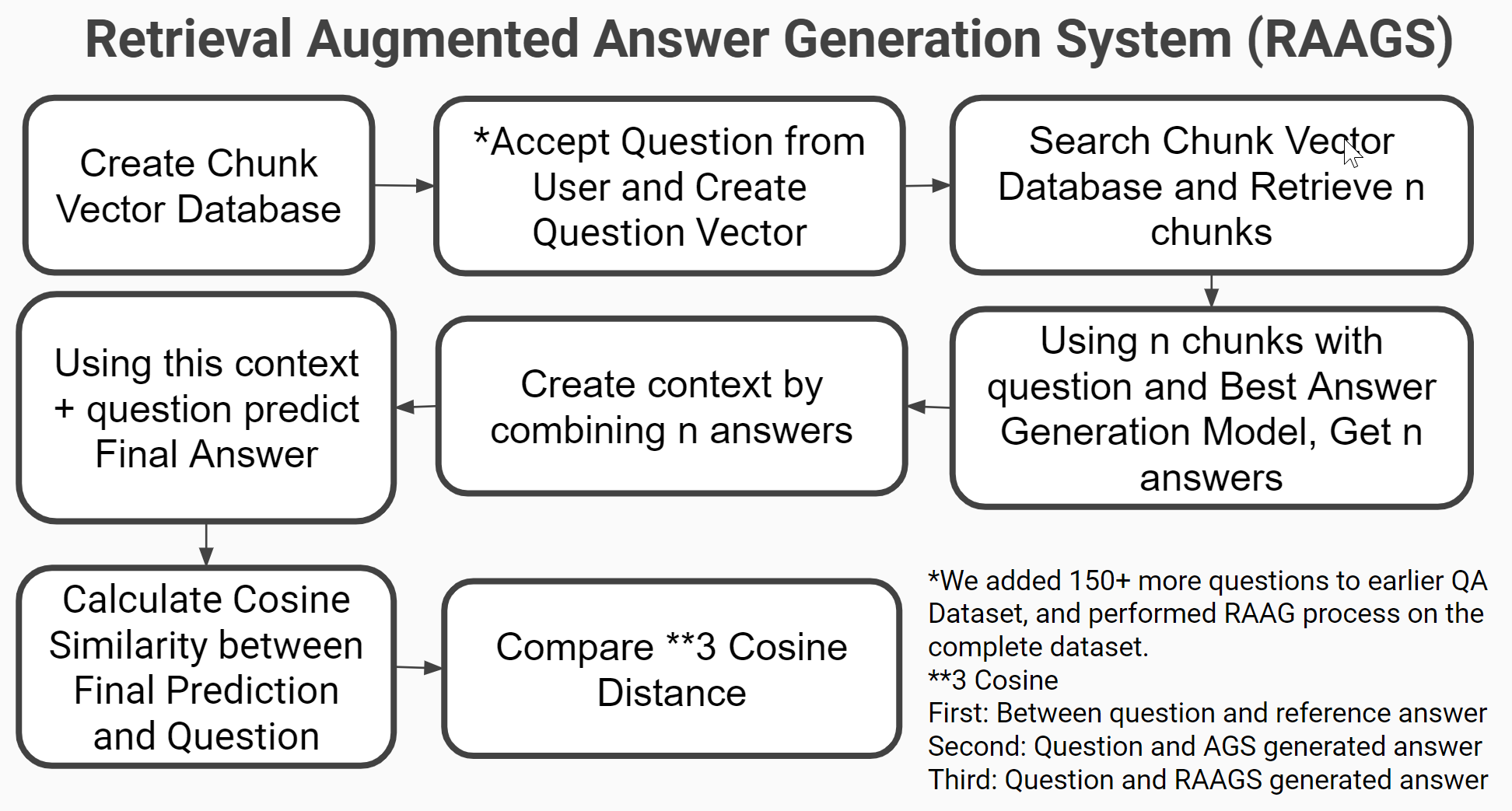
Question Answer Evaluation Metrics
Business Applications of Research Work
-
Teaching history without the physical teacher. We can create expert systems that understand history from different perspectives and help students learn the facts and context.
-
We can take the system to any domain like Banking, Insurance, Legal, and Land Records where we have a huge number of text and PDF documents. Users can interact with the system and quickly know the facts that are spread across different documents.
-
In spiritual, philosophical, and political discussions to understand the history from different viewpoints we need SME. We can take the help of HBQAS system to understand the viewpoints.
-
Archaeology sites: They can develop content for their individual sites and engage with tourists in a more entertaining and exciting way. Tourists also feel that they have learned something new about the site. In the absence of this people still go there but most of the time it is like a picnic.
-
Publication: We can create Question-Answer booklets. Rather than having plain history books with tons of stories, we can print a book in the question-answer format. Or we may develop mobile apps based on these question answers.
-
Live TV Shows: Generally television hot debate to understand the history and perspective of people sucks lots of energy and makes people bitter. An anchor can use QAGS, AGS, RAAGS to drive the debate in a more meaningful way.
-
Quiz in family, Group: People are turning towards their phones and TV, and human-to-human connection is reducing. We can discuss the topic with family members and create a quiz that they can use to play with each other in a family setup.
Implications and application of our work
-
Although we have worked using The Mahabharat Book, evaluating AI technologies for Historical Book Question Answering in the field of AI and NLP is quite interesting and has the potential to contribute to both academia and practical applications. We can extend this work to any other language or any other historical book.
-
Relevance and Significance: The historical book Question Answering is a meaningful and valuable application of AI and NLP. It can help make historical texts more accessible and understandable to a wider audience, including researchers, students, and enthusiasts.
-
Interdisciplinary Nature: Our research involves elements of AI, NLP, and history. AI and NLP are evolving fast and history is becoming more relevant to solve the current struggle, to understand the background, and to understand the value system of societies. Advancing this work can potentially lead to innovative solutions.
-
Real-World Applications: Effective historical book question-answering systems can have practical applications in education, research, and even cultural heritage preservation. Our research could bridge the gap between historical texts and how modern people understand that today.
-
Evaluation and Benchmarking: While building and evaluating our system for historical book question answering, we contribute to the understanding of what metrics should be used for evaluating this kind of work and what value we can expect for those metrics.
-
Data Quality and ChatGPT Limitations: While using ChatGPT for generating reference answers is a creative approach, we need to keep in mind that ChatGPT might not capture all nuances and historical accuracy. Manual verification or expert validation of reference answers might be required. And this become more relevant when we are doing this work around a controversial history work.
-
Ethical and Cultural Sensitivity: Historical texts like the Mahabharat contain sensitive and sacred content. We need to understand to pick up the most authentic translation for this kind of work. Or generate multiple answers and mention as per which book what answer is generated. This helps people learn different viewpoints.
-
Baseline Comparison: Our work helps us understand high dimension embedding does not mean the best sentence vector. We need to understand what kind of sentence embedding model is suitable for our work. Secondly, in the race for LLM which is expensive to train and deploy, we can still work with models like T5.
-
During Academic Class: Based on the content that was taught last week, last day, or today, a teacher can walk through the lessons with the help online quiz. These quizzes can be generated from thousands of AI-generated QA. Sometimes students ask tough questions which is not easy to answer or that need to throw the light from a different perspective. We can use AI-generated answers for this.
-
Creating Question-Answer Books: Rather than having plain history books with tons of stories, we can print a book in the question-answer format. Or we may develop mobile apps based on these question answers.
Output of this work
-
QA dataset on Mahabharat. 1850+ questions in the English Language.
-
Explored approaches for Question Answer Generation
-
Explored approaches for Answer generation from a historical book.
-
Explored metrics that can help in evaluating this kind of work.
-
Explored sentence embedding models that can be used for Indian historical books translated into English language.
-
Evaluated different SOTA Question Answering Models for Historical text and finetued models for our work.
-
Explored whether we can answer a question without any context.
-
Explored how efficient is document retrieval in the case of Indian Historical text.
Future Recommendations
-
Perform AGS experiments on LLM with more parameters and bigger size models.
-
Perform AGS experiments with more epoch
-
In QAGS, generate multiple answers to generated questions. Compare the predicted answer against all the alternative answers.
-
In DRS, create multiple high-dimensional sentence embeddings for Indian Language historical text which is translated into English. And use these embedding in DRS.
-
Create QA in Indian languages. We can translate QA generated using English language and Latin script.
-
Create a sentence embedding model for Indian script (Devanagari, Kannada, Tamil) books.
-
Create a model to predict the correct Devanagari spelling of Roman script Indian Culture name entities like names of people, places, rituals, festivals, etc. Use these spellings during the translation process.
-
In AGS, to calculate BLEU and ROUGE scores, keep only NER in reference and predicted answers.
-
In DRS, take multiple books on multiple topics of the same domain say history. Create smaller chunks and chunk vectors to understand how DRS works
-
In RAAGS, accept questions from multiple books and multiple topics.
-
In RAAGS, instead of joining multiple answers, stuff the original chunks using langchain and pass that final chunk to AGS, to get the answer.
-
Human-in-the-Loop Evaluation: Given the unique nature of the historical text, involving domain experts or historians in the evaluation process could provide valuable insights and enhance the quality of the evaluation.
-
Types of Questions: In our work, we have explored open-ended answers but we can take this work forward for other formats like fill-in-the-blank, and MCQ.
-
The QA dataset created in this project can be translated into other Indian Languages. For that purpose, we need to do NER on the English text. Get the correct spelling of the word. Roman language has a limitation in writing Sanskrit names correctly. Due to this reason when Indian language text is translated into English language noun spelling becomes wrong. For example, Yagnya, Pruthuvi, Sravanan, Ramayan, Ram, Krushna these words have sounds that are not in European languages hence these words are wrongly written in Roman script.
Research Report
Details report is available on the request.